
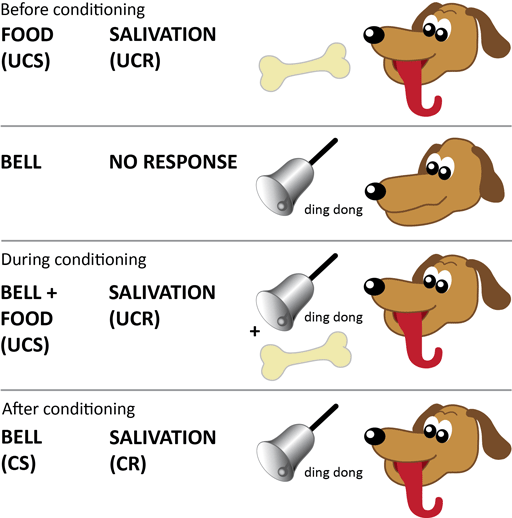
Salivating to food in the mouth is reflexive, so no learning is involved. Over time, Pavlov (1927) observed that the dogs began to salivate not only at the taste of food, but also at the sight of food, at the sight of an empty food bowl, and even at the sound of the laboratory assistants’ footsteps. He then measured the amount of saliva produced in response to various foods. In his studies with dogs, Pavlov surgically implanted tubes inside dogs’ cheeks to collect saliva. Pavlov’s area of interest was the digestive system (Hunt, 2007). Physiologists study the life processes of organisms, from the molecular level to the level of cells, organ systems, and entire organisms. Pavlov was a physiologist, not a psychologist. Pavlov came to his conclusions about how learning occurs completely by accident. Ivan Pavlov’s research on the digestive system of dogs unexpectedly led to his discovery of the learning process now known as classical conditioning. As we discussed briefly in the previous section, classical conditioning is a process by which we learn to associate stimuli and, consequently, to anticipate events. Pavlov (1849–1936), a Russian scientist, performed extensive research on dogs and is best known for his experiments in classical conditioning (Figure 1). Identify the NS, UCS, UCR, CS, and CR in classical conditioning situationsĭoes the name Ivan Pavlov ring a bell? Even if you are new to the study of psychology, chances are that you have heard of Pavlov and his famous dogs.Explain how classical conditioning occurs.For instance, providing consistent reassurance and support may help a child who is anxious about reading aloud start to feel more calm and comfortable. Teachers can use classical conditioning to help children overcome some anxiety-provoking contexts. For instance, if a particular bell tone is the conditioned stimulus, similar sounding bell tones can elicit the same response. Once a conditioned response has been created, it can tend to emerge as a response to other stimuli which appear similar. For a conditioned response to be maintained, the unconditioned stimulus must be re-introduced occasionally to ‘top up’ the desired conditioned response. ExtinctionĮxtinction (the opposite of acquisition) occurs when a conditioned response weakens or ceases to exist. This must then be repeatedly reinforced to ensure strong learning takes place. AcquisitionĪcquisition requires a neutral stimulus to become linked with an unconditioned stimulus. The key elements of classical conditioning: 1. That means the subject has learned to produce the CR when triggered by the CS – which was previously just a neutral signal. At this final stage, the response has now become a CR (conditioned response). One the UCS and the CS are connected, the CS alone will trigger a response.
/2794863-operant-conditioning-a21-5b242abe8e1b6e0036fafff6.png)
Once this starts to happen, the neutral stimulus is transformed into a CS (conditioned stimulus) because the subject has now become conditioned to respond to the CS as if it were the natural UCR. Soon, the neutral stimulus becomes linked with the UCS. Next, a neutral stimulus is repeatedly introduced alongside the UCS. So at this stage, there is a UCS (unconditioned stimulus) linked to a UCR (unconditioned response) which occurs naturally. The action of classical conditioning upon a subject is a three-phase process: Phase 1: Pre-conditioned stateĬlassical conditioning demands a naturally occurring stimulus which will induce an automatic response.

Once the sound of the neutral stimulus became linked to the stimulus present in the environment (food arriving), it soon became possible to induce salivating just by sounding the neutral stimulus. For instance, Pavlov’s dogs heard a tone (neutral stimulus) followed by salivating (naturally occurring reflex) in response to the arrival of food. For learning to occur, there must also be a ‘neutral stimulus’ which is then followed by a naturally occurring reflex. Ivan Pavlov Theory: Classical Conditioningįirst discovered by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936), classical conditioning is a learning process governed by associations between an environmental stimulus and another stimulus which occurs naturally.Īll classical conditioned learning involves environmental interaction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
